Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept—it is an integral part of our daily lives, and its influence on various industries is profound. Workforce automation is one of the key areas where AI is having a big influence. The integration of AI in the workplace has the potential to revolutionize how businesses operate, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and driving innovation. However, it also raises important questions about the future of work, job displacement, and the skills required in an AI-driven economy.
Definition
Artificial intelligence is the term used to describe how technology, especially computer systems, mimic human intellectual functions. Learning (the process of acquiring knowledge and applying rules to it), reasoning (using rules to arrive at broad or precise conclusions), and self-correction are some examples of these processes. Natural language processing, robotics, computer vision, machine learning, and other subfields are all included in the umbrella of artificial intelligence. The goal of AI/ML Development Services is to build intelligent computers that, like humans, can sense their surroundings, gain knowledge from past experiences, and decide for themselves or solve problems.
The Evolution of AI in Workforce Automation
AI’s role in workforce automation has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, automation was limited to repetitive, rule-based tasks such as manufacturing and data entry. These tasks were automated using simple algorithms and mechanical systems. However, with advancements in machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics, AI can now perform complex tasks that require cognitive abilities, such as decision-making, problem-solving, and even creative thinking.
The rise of AI-driven automation can be categorized into three phases:
Rule-Based Automation: The earliest form of automation, where machines followed predefined rules to perform tasks. This phase focused on increasing efficiency in repetitive tasks.
Machine Learning-Based Automation: With the advent of machine learning, AI systems could analyze large datasets, learn patterns, and make predictions. This phase allowed automation to expand into areas such as customer service, finance, and Machine Learning in Healthcare.
Cognitive Automation: The latest phase, where AI systems can understand, reason, and interact with humans in natural language. Cognitive automation enables AI to take on more complex roles, such as virtual assistants, chatbots, and autonomous vehicles.
Benefits of AI-Driven Workforce Automation
AI-driven automation offers several benefits that can significantly enhance business operations and overall productivity. These include:
- Increased Efficiency: AI can perform tasks faster and more accurately than humans, reducing the time and effort required to complete them. This leads to higher productivity and allows businesses to scale operations without a corresponding increase in labor costs.
- Cost Reduction: By automating routine tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs and minimize errors, leading to significant cost savings. AI-driven automation can also optimize resource allocation, reducing waste and improving profitability.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, providing insights that help businesses make informed decisions. This capability is particularly valuable in areas such as finance, marketing, and supply chain management.
- Improved Customer Experience: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24/7 customer support, answer queries, and resolve issues quickly. This enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to increased revenue.
- Innovation and Creativity: AI can take over routine tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on creative and strategic activities. This shift allows businesses to innovate and stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
Challenges and Concerns
While AI-driven workforce automation offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges and concerns that need to be addressed:
- Job Displacement: One of the most significant concerns is the potential loss of jobs due to automation. AI can replace human workers in various roles, leading to unemployment and economic disparity. Industries such as manufacturing, retail, and transportation are particularly vulnerable to job displacement.
- Skills Gap: As AI takes over routine tasks, the demand for highly skilled workers who can develop, manage, and maintain AI systems increases. This creates a skills gap that needs to be bridged through education and training programs.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI in decision-making raises ethical concerns, particularly in areas such as hiring, lending, and law enforcement. Inadvertently maintaining biases found in the data that AI systems are educated on could result in biassed decisions.
- Data Privacy and Security: For AI systems to work well, huge amounts of data are required. This raises concerns about data privacy and security, as sensitive information could be exposed or misused.
- Regulatory and Legal Challenges: There are legal and regulatory issues arising from the workplace’s quick adoption of AI. Governments and regulatory bodies need to establish clear guidelines. To ensure that AI is used responsibly and does not harm workers or consumers.
The Work of the Future in an AI-Powered Economy
As AI continues to advance, the future of work will undergo significant changes. Understanding these changes and preparing for them is crucial for businesses and workers alike.
- Shift in Job Roles: While AI will replace certain jobs, it will also create new roles that require different skill sets. Jobs that involve creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence are less likely to be automated and will become more valuable.
- Lifelong Learning and Reskilling: The pace of technological change means that workers will need to continually update their skills to stay relevant. Lifelong learning and reskilling will become essential as workers transition to new roles in an AI-driven economy.
- Human-AI Collaboration: AI and humans will probably need to operate closely together in the workplace of the future. Rather than replacing humans, AI will augment human capabilities, allowing workers to focus on tasks. That require creativity, empathy, and complex problem-solving.
- Redefining Work-Life Balance: As AI takes over more tasks, the traditional 9-to-5 workday may become obsolete. Workers may have more flexibility in how and when they work, leading to a better work-life balance.
- Social and Economic Implications: The widespread adoption of AI-driven automation will have broader social and economic implications. Governments, businesses, and communities will need to work together to address issues such as income inequality, access to education, and social safety nets.
Preparing for an AI-Driven Future
To harness the benefits of AI-driven automation while mitigating its challenges, businesses, workers, and policymakers must take proactive steps:
- Invest in Education and Training: To ensure that workers have the skills necessary in an AI-driven economy, firms and governments alike should invest in education and training initiatives. This includes both technical skills, such as coding and data analysis, and soft skills, such as creativity and communication.
- Foster a Culture of Innovation: Businesses should encourage a culture of innovation that embraces AI as a tool for growth and improvement. This involves rethinking traditional business models and exploring new ways to integrate AI into operations.
- Develop Ethical AI Practices: To ensure that AI is used responsibly, businesses should develop ethical guidelines for AI development and deployment. This includes addressing biases in AI systems, protecting data privacy, and ensuring transparency in AI decision-making.
- Promote Collaboration Between Humans and AI: Rather than viewing AI as a threat, businesses should focus on how AI can complement human workers. This involves designing AI systems that enhance human capabilities and create a more collaborative work environment.
- Engage in Policy Discussions: Policymakers should engage in discussions about the impact of AI on the workforce and develop regulations that protect workers while promoting innovation. This includes exploring options such as universal basic income, social safety nets, and policies that encourage lifelong learning.
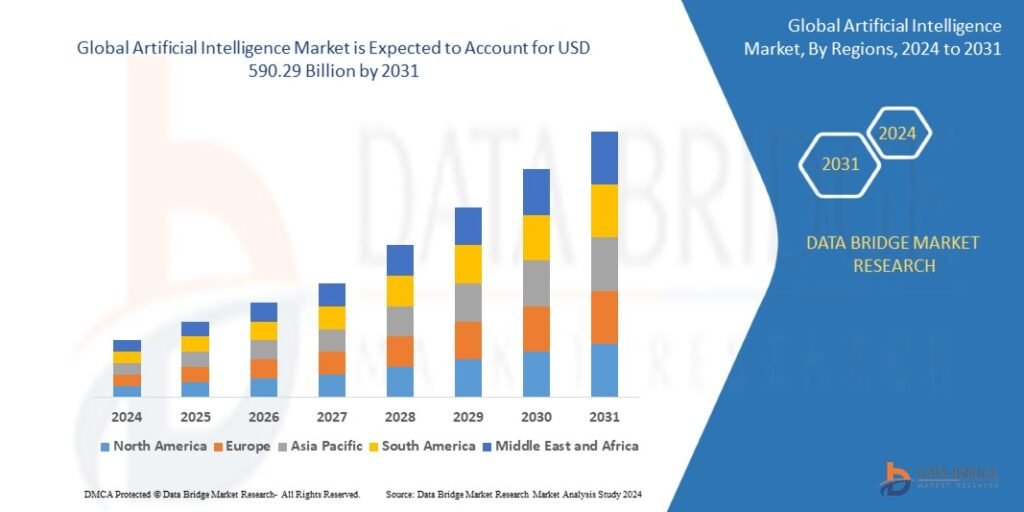
Growth Rate of Artificial Intelligence Market
The size of the global artificial intelligence market was estimated to be worth USD 92.33 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.1% to reach USD 590.29 billion by 2031.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-artificial-intelligence-market
Conclusion
AI-driven workforce automation is transforming the way businesses operate and the nature of work itself. While it offers significant benefits in terms of efficiency, cost reduction, and innovation. It also presents challenges that need to be addressed. By investing in education, fostering innovation, and developing ethical AI practices, businesses and policymakers can ensure that the transition to an AI-driven economy is smooth and inclusive. The future of work will involve a new paradigm where humans and AI work together to achieve greater heights, creating opportunities for growth, creativity, and progress.